All Using Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
Updated:June 16, 202510 min read
Cybercriminals don't waste any time and the number of cyberattacks is growing every year. According to NordLayer, Amazon now tracks hundreds of millions more potential cyber threats daily. It went from 100 million to 750 million threats per day in just six or seven months.
Intro
Cyberattacks are becoming more and more intense. Even their complexity grows, as they are carried out in several directions at once. Cybercriminals are using AI and ML, to carry out these attacks. They quickly adapt to vulnerability patches and effectively manage their attempts.
In response, cybersecurity teams now apply AI and machine learning to spot and stop threats. AI’s edge is speed – analyzing torrents of data in moments and learning from each attack. If you’re planning similar defenses, talk to our AI solution experts about crafting the right stack. In addition, AI can learn from experience — this is the essence of machine learning.
In this article, SapientPro’s experts will share how AI helps in cybersecurity and its effect on the future development trends in this industry. Read on for professional insights!
What is AI in Cybersecurity?
Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity refers to intelligent systems that enhance digital security by detecting, analyzing, and responding to cyber threats in real-time. These systems use machine learning algorithms to identify patterns in data, predict potential security breaches, and automate threat responses.
Only the best machine learning (ML) programming languages are used for the highest effectiveness of the developed solutions.
Unlike traditional security tools that rely on predefined rules, AI cybersecurity applications continuously learn from new threats and adapt their defense mechanisms. They offer more dynamic and preventative protection against evolving cyberattacks.

Role of AI in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity experts view AI as an algorithm that can find patterns in input data or evaluate it to use the results to make decisions on its own. AI should act like a human, following the principle of “observe, orient, decide, act” (OODA). At the same time, a “robot” can do it hundreds of times faster than a human.
The first AI-based cybersecurity tools started to be used back in the late 1980s. These were cyber threat warning systems based on predetermined rules and parameters. In the 2000s, the role of AI began to grow, primarily due to advances in machine learning. But the real breakthrough for AI in cybersecurity was provided by the rapid development of neural networks and generative AI in recent years.
Today, generative AI in cybersecurity has already become a double-edged blade that can be both the greatest threat and the most effective defense. It all depends on whose hands this tool is in.
Unfortunately, hackers have mastered AI technologies very quickly and are actively using them for cyberattacks in a number of ways:
- Automating the processes of tampering (finding vulnerabilities, overcoming defenses);
- Simplifying and automating targeted phishing for identity theft;
- Making deepfakes for fraud and social engineering;
- Data poisoning to disable AI models for any task;
- Simplifying malware development.

These new threats are forcing the cyber defense industry to urgently adapt and widely deploy appropriate AI algorithms to:
- Monitor suspicious activity;
- Find vulnerabilities in systems;
- Assess risks;
- Recognize AI-generated material;
- Instantly respond to attacks.
As a result, the adoption of AI-based cybersecurity is evolving extremely fast. According to Spherical Insights, in 2022, the global AI solutions market for cybersecurity was estimated at $15.25 billion, and by 2032, it is projected to reach $96.81 billion.
It is expected that during the forecast period this sphere will grow at an average annual growth rate of 20%. In fact, in two to three years, it will be impossible to imagine cybersecurity without machine learning algorithms and neural networks.
Use of AI in Cybersecurity: What Can It Do?
Let’s check out the best AI in cybersecurity examples. We’ll cover how modern companies use artificial intelligence to protect their businesses.
Malware Analysis
Signature analysis has been the main feature used in antivirus software for many years. This method consists of identifying the characteristic properties of each virus and searching for viruses by comparing files with the identified properties.
This algorithm can be implemented in both assembly and high-level languages. Using a compiler or interpreter ensures the differences are insignificant, maintaining the efficiency of both options. But don't forget about various obfuscators, which can also change malware code beyond recognition.
In this case, classical signature analysis will not help us much. And this is where artificial intelligence comes to our aid. While some people may think of sandboxes, which are also an effective tool for detecting malware, deploying a sandbox requires large software and hardware resources. Most importantly, it requires time. Using AI significantly reduces the time and resources required..
Information Security Events Analysis
This point is especially relevant for SaaS security. The traditional means of collecting and analyzing information security events are SIEM (Security Information Event Management) solutions. SIEM performs centralized collection and analysis of events for compliance with certain correlation rules.
The fact is that the analysis of a large volume of events (tens of thousands of events per second) is a rather resource-intensive task. The use of classical correlation rules that implement logic similar to the one shown in the picture may require large capacities.

And besides, ordinary rules have binary logic. A set of events either fall or don't fall under certain conditions, and if they don't, an alert won't be generated. AI can make the logic more intelligent and thus make the detection of suspicious activity more efficient.
Behavior Analysis
Code analysis using various methods allows us to detect various types of malicious applications, both already known and yet unknown, but behaving suspiciously. However, in addition to viruses, Trojans, and other backdoors, we may also encounter various hacking tools, exploits for zero-day vulnerabilities, and attempts to use legitimate system software for various hacking activities.
Not all such activities can be detected by antivirus. This is because here, we need to analyze not just code signatures but the behavior of the user and applications in the system: who launches certain processes, when, and for what purpose.

In the image, we can see three groups of applications: “Bad”, “Good” and “Gray”. The gray zone applications tend to be in the majority.
To detect suspicious activity, EDR (Endpoint Detection & Response) systems place agents on user nodes that collect the necessary information about running processes, system changes, new settings, etc. However, the problem here is similar to correlation rules in SIEM: it is too difficult to describe all possible suspicious activities with rules.
This is also where AI in cybersecurity comes to our aid, allowing us to identify potential malicious activity based on data about legitimate and suspicious behavior received from agents. In particular, we can detect the compromise of a legitimate application infected with some malware or suspicious behavior of a PowerShell script run by a legitimate user.
We can also include analysis of network traffic and detection of suspicious packets (IDS functionality), as well as behavior and malware analysis. Here, AI in cybersecurity can help identify various attacks in traffic, both at the lower levels of the hierarchical model and at the application level.
Antifraud
Fraud detection systems are another important area of cybersecurity that is actively used in banking and finance. These systems are used to mitigate risks and ensure fraud security in line with the interests of customers and financial organizations.
Such systems detect deviations in transactions and score them by measuring deviation ratios. However, classical scoring models have a high false positive rate. For example, a series of several transfers from a legal entity to several individuals may appear fraudulent to the system.
AI in cybersecurity here can effectively analyze the flow of transactions, identifying potentially suspicious ones. Building AI software from scratch is very beneficial for financial institutions.
Prescriptive Analytics
Above, we looked at a few areas of cybersecurity where artificial intelligence can be used quite effectively. In addition to these areas, AI can also be actively used when there is a need to predict certain events.
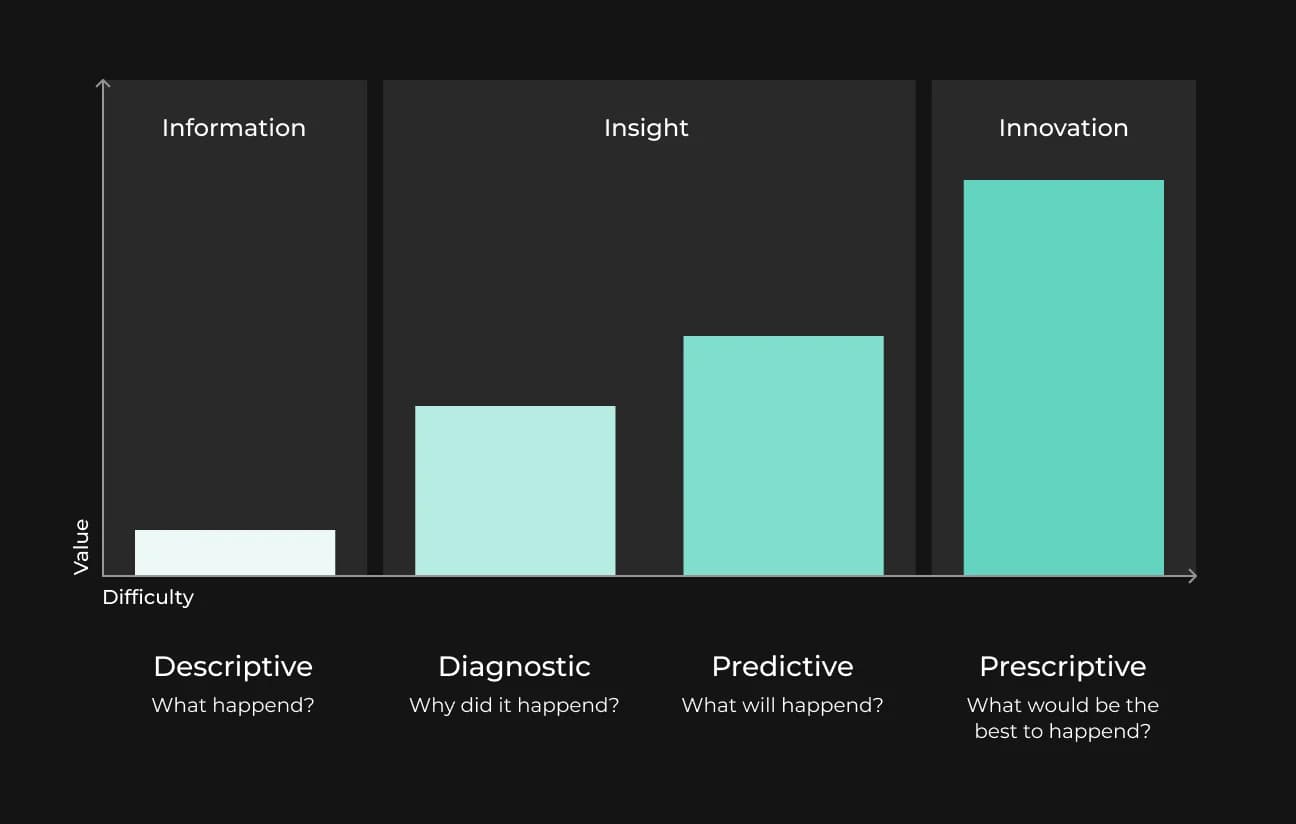
Prescriptive analytics is another cutting-edge area for machine learning that deserves mention from a cybersecurity perspective. Unlike predictive analytics, which predicts a threat by comparing current events to historical threat logs, prescriptive analytics is a more operational process. Prescriptive analytics deals with situations where a cyberattack has already begun. At this stage, it analyzes the data to suggest what response can best fit the situation to minimize information loss.
AI is best suited to perform prescriptive analysis effectively. This is because it is extremely difficult to perform this kind of prediction using classical rules. With prescriptive analysis, we can detect attacks before they happen.
Use Cases for AI in Cybersecurity
Here are 4 practical AI in cybersecurity use cases for specific challenges.
Protection Against Botnet Attacks for Small Businesses
Problem. Small businesses often face botnet attacks that can disable their websites and online services.
Solution. Using AI, it is possible to analyze traffic and identify anomalies typical of botnet attacks. AI systems can automatically block suspicious IP addresses and prevent access to company resources.
AI in cybersecurity benefits for this case:
- Increased resilience of websites and online services;
- Reducing the risk of lost revenue due to inoperable websites;
- Automation of the protection process is especially important for small companies with limited resources.
Detection and Prevention of Data Breaches on Corporate Networks
Problem. Data breaches can cause significant damage to a company's reputation and financial health.
Solution. AI systems can monitor network activity and analyze user behavior. They can detect unusual activity, such as mass data copying or attempts to access sensitive information, and automatically block suspicious transactions.
AI in cybersecurity benefits for this case:
- Reducing the risk of data breaches and associated losses;
- Increased protection of sensitive information;
- Automatic response to suspicious activity, allowing threats to be prevented more quickly.
Protection Against Targeted Attacks on Healthcare Facilities
Problem. Healthcare facilities are often the target of cyberattacks, which can result in the leakage of patient data and disruption of systems.
Solution. AI protects medical systems and databases. Additionally, artificial intelligence can analyze user behavior and data access, identifying unauthorized access attempts or suspicious activity. It can also automate the process of updating security systems and applying patches.
AI in cybersecurity benefits for this case:
- Increasing the level of protection of patients' personal data;
- Ensuring uninterrupted operation of medical systems;
- Reducing the risk of financial and reputational losses for medical institutions.
Protection Against Attacks on the Internet of Things (IoT) in Smart Homes
Problem. IoT devices in smart homes are often subject to cyberattacks, which can lead to data leakage and device disruption.
Solution. AI can monitor and protect IoT devices. It can be used to analyze network traffic and device behavior, identifying anomalies and automatically blocking suspicious activity. AI can also provide regular updates and security checks on devices.
AI in cybersecurity benefits for this case:
- Increasing the security of smart homes;
- Reducing the risk of data breaches and hacking of IoT devices;
- Automation of the protection process, which is convenient for end users.
Summary
Currently, the number of AI-based cybersecurity solutions is growing, and their importance will only grow over time. We see a significant evolution of AI in cybersecurity.
That said, AI is particularly good at collecting and analyzing massive amounts of data, extracting valuable information, and responding accordingly. These capabilities greatly enhance an organization's ability to detect and respond to cyberattacks and ultimately minimize the potential damage caused by attackers.
The main tasks that AI can perform are:
- Detection;
- Prediction;
- Automation;
- Response;
- Adaptation based on previous findings.
As you can see, AI can solve quite a large set of cybersecurity tasks, and this list will only grow in the future. Future of AI in cybersecurity is bright. If you want to keep up with its development trends, partner with SapientPro for custom AI solution development. You'll get 8+ years of experience in your project that will get you end-to-end support. Let's team up now!